Le certificat SSL Let's Encrypt est fourni GRATUIT dans tous nos forfaits d'hébergement Web.
DétailPerformances complètes, matériel complet, solutions de location de serveurs pour tous les budgets.
DetailLe certificat SSL Let's Encrypt est fourni GRATUIT dans tous nos forfaits d'hébergement Web.
DétailPerformances complètes, matériel complet, solutions de location de serveurs pour tous les budgets.
Detail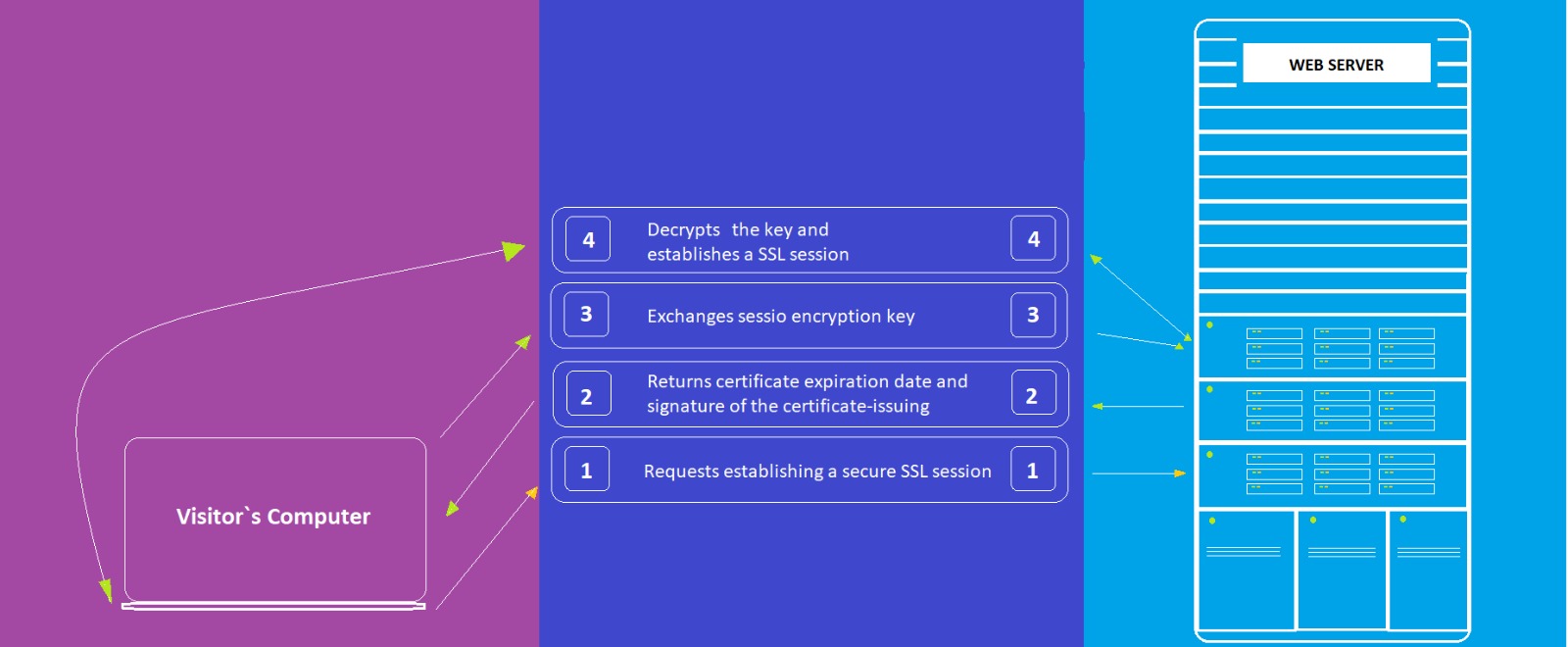
You probably already know Comodo SSL Certificates deliver the highest standard of security for websites across the world. But if you’re looking for the best Comodo SSL price too, you’ve landed in the right place.
Now you can give your visitors and customers the peace of mind they deserve through our selection of top-notch Comodo SSL Certificates, to suit every type of website and budget. Your cheap SSL Comodo search is over.
Your website’s visitors need to be able to trust in you and your online presence. Data security and online fraud has never been more front-of-mind. By choosing a Comodo SSL, you will show the world your site can be trusted (with the padlock or green bar) right from the URL. Today’s web visitors are looking for signs of your security, and they don’t do second chances. In fact, they don’t even do first chances either!
By investing in a Comodo SSL, You will be joining millions of happy and secure customers around the world. Comodo has issued over 100 million certificates across more than 150 countries. So whether your website is a simple set up, or a turbocharged ecommerce heavyweight, make sure you’re investing in the right SSL certificate at the right price… to satisfy more customers the right away.
Snap up one of our amazing SSL Comodo deals now.
SSL certificates must be installed on your web server. Therefore, an end-to-end SSL installation support is possible only in cases where the domain name is hosted with Namecheap. If the domain is hosted with any other provider, please contact their support team for assistance with CSR generation and SSL installation.
Selected orders may be flagged for an additional "Brand Validation" procedure by the Certificate Authority. This is a necessary security measure. If the order is flagged for Brand Validation, SSL issuance will be delayed for a period of time deemed necessary by the Certificate Authority.
EVs are certificates with extended validation. In 2006, the CA / Browser Forum, a group of leading certificate vendors and browser developers (CA) or Certificate Authorities (CAs), approved several standard guidelines for issuing and validating EV certificates. . Thus, the way the EV certificate is displayed has been changed so that the visitor can more easily recognize that this website has a higher standard of security. These certificates are displayed with an additional green bar, which distinguishes them from other certificates, which are displayed in plain blue or green at the address.
With such a certificate, owners can protect themselves from counterfeiters who want to steal their brand and customers.
1. The institutions that can purchase and apply for an EV certificate are the following:
The documents required to issue the SSL certificate must include the following:
2. Requirements for the domain on which the SSL certificate will be installed:
3. Requirements from the person requesting the SSL certificate:
4. As an additional check for the organization, a telephone check with a responsible person of this organization is required. The telephone check is carried out directly by the issuing authority. During the telephone check, you will be required to do the following:
 Copyright © 2020 Tous droits réservés
Copyright © 2020 Tous droits réservés
 Worldwide (English)
Worldwide (English) Romania (Romanian)
Romania (Romanian) Spain (Spanish)
Spain (Spanish) Germany (German)
Germany (German) France (French)
France (French) Bulgaria (Bulgarian)
Bulgaria (Bulgarian) Indonesia (Indonesian)
Indonesia (Indonesian) Portugal (Portuguese)
Portugal (Portuguese) South Africa (Zulu)
South Africa (Zulu)